Current Economic Statistics and Review For the
Week
Ended April 8, 2006
Theme
of the week:
Services Sector Exports: Growth and Prospects**
One
of the most significant developments in the 1990’s, pertaining to our
exports of goods and services, has been a remarkable growth in services
transactions with the rest of the world. Over the years,
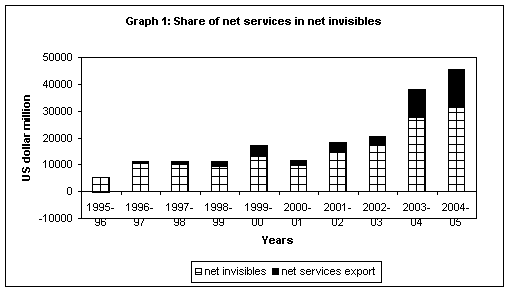
Among the various items of invisibles1, services export receipts have risen from 46.7 per cent of total invisible receipts in 1995-96 to 64.1 per cent in 2004-05 and services receipts as per cent of total current receipts has doubled from 15 per cent in 1995-96 to around 30 per cent in 2004-05 (Annexure A). From a negative contribution to net invisibles in 1995-96, the share of net services export has moved up considerably and in 2004-05 it added 45.5 per cent to net invisibles as can be seen in Table 1.
|
Table
1: Share of net services exportin net invisibles |
|||
|
(US
dollar million) |
|||
|
Years |
net |
net
services |
per
cent |
|
|
exports |
share |
|
|
1995-96 |
5460 |
-186 |
-3.4 |
|
1996-97 |
10321 |
851 |
8.2 |
|
1997-98 |
10007 |
1319 |
13.2 |
|
1998-99 |
9208 |
2165 |
23.5 |
|
1999-00
|
13143 |
4064 |
30.9 |
|
2000-01 |
9794 |
1692 |
17.3 |
|
2001-02 |
14974 |
3324 |
22.2 |
|
2002-03 |
17035 |
3643 |
21.4 |
|
2003-04 |
27801 |
10144 |
36.5 |
|
2004-05 |
31229 |
14199 |
45.5 |
|
Source:
same as Annexure A |
|
||
Profile
of Services Export
Table
2 gives the profile of services export. Major heads of services in the
|
Table
2. Structure of |
|||||||
|
Year |
Services
Exports (US
$ million) |
Per
cent share in Total Services Exports |
|||||
|
|
|
Travel |
Transportation |
Insurance |
GNIE |
Software |
Miscellaneous* |
|
1970-71 |
292 |
16.8 |
49.7 |
5.5 |
13.7 |
0 |
14.4 |
|
1980-81 |
2804 |
43.5 |
16.3 |
2.3 |
4.0 |
0 |
33.9 |
|
1990-91 |
4551 |
32.0 |
21.6 |
2.4 |
0.3 |
0 |
43.7 |
|
1995-96 |
7357 |
36.9 |
27.3 |
2.4 |
0.2 |
0 |
33.2 |
|
2000-01 |
16268 |
21.5 |
12.6 |
1.7 |
4.0 |
39.0 |
21.3 |
|
2001-02 |
17140 |
18.3 |
12.6 |
1.7 |
3.0 |
44.1 |
20.3 |
|
2002-03 |
20763 |
16.0 |
12.2 |
1.8 |
1.4 |
46.2 |
22.4 |
|
2003-04 |
26868 |
18.7 |
11.9 |
1.6 |
0.9 |
47.6 |
19.2 |
|
2004-05 |
46031 |
14.1 |
10.4 |
2.0 |
0.7 |
37.4 |
35.4 |
|
Notes:
* Excluding software services, GNIE: Government not included
elsewhere Source:
RBI, Annual Report, 2004-05 |
|||||||
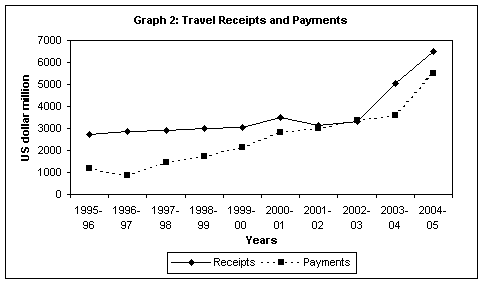
Travel
Travel
represents all expenditure by foreign tourists in
|
Table
3: |
||||
|
(US
Dollar million) |
||||
|
Year |
Receipts |
Payments |
Net
Receipts |
Foreign
Tourist arrivals (million
no.) |
|
1995-96 |
2713 |
1167 |
1546 |
|
|
1996-97 |
2878 |
858 |
2020 |
2.33 |
|
1997-98 |
2914 |
1437 |
1477 |
2.37 |
|
1998-99 |
2993 |
1743 |
1250 |
2.40 |
|
1999-00 |
3036 |
2139 |
897 |
2.52 |
|
2000-01 |
3497 |
2804 |
693 |
2.67 |
|
2001-02 |
3137 |
3014 |
123 |
2.43 |
|
2002-03 |
3312 |
3341 |
-29 |
2.45 |
|
2003-04 |
5037 |
3602 |
1435 |
2.87 |
|
2004-05 |
6495 |
5510 |
985 |
3.50 |
|
Source:
RBI Bulletin (various issues) and Ministry of Tourism |
||||
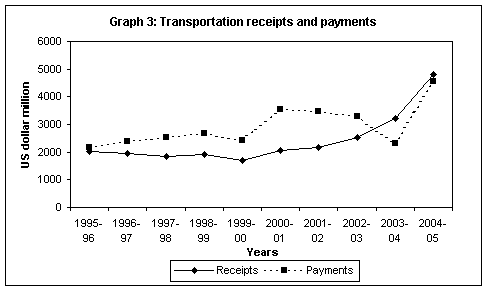
Transportation
Transportation
records receipts and payments on account of the carriage of goods, persons
as well as other distributive services (like port charges, bunker fuel,
warehousing etc.) performed on merchandise trade. Annexure
B provides with the detailed transportation account and it can
be seen that on the receipts front ‘freight on exports’ is the major
contributor.
|
Table
4: |
|
|||
|
(US
dollar million) |
|
|||
|
Years |
Receipts |
Payments |
Net
|
|
|
1995-96 |
2011 |
2163 |
-152 |
|
|
1996-97 |
1953 |
2394 |
-441 |
|
|
1997-98 |
1836 |
2522 |
-686 |
|
|
1998-99 |
1925 |
2680 |
-755 |
|
|
1999-00
|
1707 |
2410 |
-703 |
|
|
2000-01 |
2046 |
-1512 |
||
|
2001-02 |
2161 |
3467 |
-1306 |
|
|
2002-03 |
2536 |
3272 |
-736 |
|
|
2003-04 |
3207 |
2328 |
879 |
|
|
2004-05 |
4798 |
4539 |
259 |
|
|
Source:
Same as Annexure
A |
|
|||
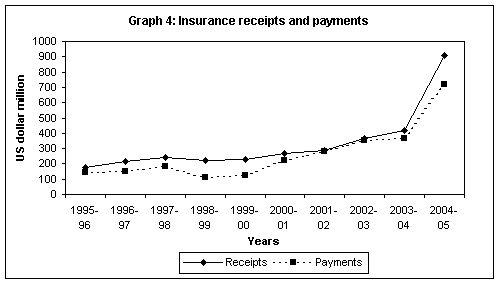
Insurance
Insurance
receipts consist of insurance on exports, premium on life and non-life
policies and reinsurance premium from foreign insurance companies.
Insurance on exports has the maximum share in the total insurance receipts
and is directly linked to total exports from
|
Table
5: |
|||
|
(US
dollar million) |
|||
|
Years |
Receipts |
Payments |
Net
|
|
1995-96 |
179 |
143 |
36 |
|
1996-97 |
217 |
153 |
64 |
|
1997-98 |
240 |
183 |
57 |
|
1998-99 |
224 |
112 |
112 |
|
1999-00
|
231 |
122 |
109 |
|
2000-01 |
270 |
47 |
|
|
2001-02 |
288 |
280 |
8 |
|
2002-03 |
369 |
350 |
19 |
|
2003-04 |
419 |
363 |
56 |
|
2004-05 |
909 |
722 |
187 |
|
Source:
Same as Annexure
A |
|||
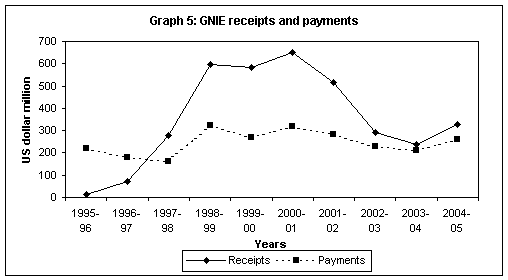
Government
Not Included Elsewhere
‘Government
not included elsewhere’ receipts represent inward remittances towards
maintenances of foreign embassies, diplomatic missions and
international/regional institutions in
|
Table
6: |
|||
|
(US
dollar million) |
|||
|
Years |
Receipts |
Payments |
Net
|
|
1995-96 |
13 |
218 |
-205 |
|
1996-97 |
72 |
178 |
-106 |
|
1997-98 |
276 |
160 |
116 |
|
1998-99 |
597 |
325 |
272 |
|
1999-00
|
582 |
270 |
312 |
|
2000-01 |
651 |
332 |
|
|
2001-02 |
518 |
283 |
235 |
|
2002-03 |
293 |
228 |
65 |
|
2003-04 |
240 |
212 |
28 |
|
2004-05 |
328 |
261 |
67 |
|
Source:
Same as Annexure
A |
|
||
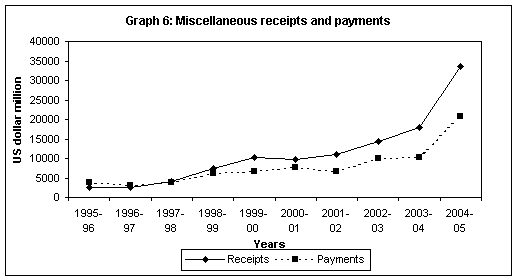
Miscellaneous
Miscellaneous services encompass communication services, financial services, software services, construction services, news agency services, royalties, copyrights and license fees, management services and others. Since 2000-01, software services are shown as a separate sub-item under miscellaneous services in the BoP and have the largest share.
During
1990s miscellaneous services at the back of a massive spurt in software
service export and aided in general by the climate of progressive
liberalisation emerged as the major driver behind services sector export
growth and the largest contributor in the total as well as net services
export (Annexure
A). It has also emerged as one of the major constituent of net
invisibles. However, at the same time,
payments for communication services, construction services, financial
services, royalties, copyrights and license fee and other services have
also risen. There is a significant outflow on account of other services.
During 2004-05, two-third of the total service payments by
Table
5:
|
|||
|
(US
dollar million) |
|||
|
Years |
Receipts |
Payments |
Net
|
|
1995-96 |
2441 |
3846 |
-1405 |
|
1996-97 |
2479 |
3165 |
-686 |
|
1997-98 |
4163 |
3808 |
355 |
|
1998-99 |
7447 |
6161 |
1286 |
|
1999-00
|
10153 |
6704 |
3449 |
|
2000-01 |
9804 |
2132 |
|
|
2001-02 |
11036 |
6772 |
4264 |
|
2002-03 |
14253 |
9929 |
4324 |
|
2003-04 |
17965 |
10219 |
7746 |
|
2004-05 |
33501 |
20800 |
12701 |
|
Source:
Same as Annexure
A |
|||
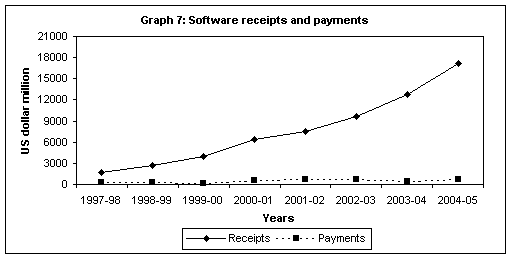
Software
Exports
An
important development of the 1990s was the emergence of software service
sector as a dynamic area of export activity, resulting from IT revolution.
Software services (with an average share of around 50 per cent in net
invisible earnings for the past 4 years), have surfaced as an important
source of miscellaneous earnings, contributing substantially to total
services receipts with gross as well as net earnings from software exports
rising steadily. Within this sector, ![]()
|
Table
6: |
|||
|
(US
dollar million) |
|||
|
Years |
Receipts |
Payments |
Net |
|
1997-98 |
1760 |
223 |
1537 |
|
1998-99 |
2626 |
348 |
2278 |
|
1999-00 |
4016 |
138 |
3878 |
|
2000-01 |
6341 |
591 |
5750 |
|
2001-02 |
7556 |
672 |
6884 |
|
2002-03 |
9600 |
737 |
8863 |
|
2003-04 |
12800 |
476 |
12324 |
|
2004-05 |
17200 |
674 |
16526 |
|
Source:
Same as Annexure
A |
|
||
Services
Exports: A Renewed Focus
The
rising importance of trade in invisibles has also been reflected in the
country’s trade policy. The services sector has been identified as a
thrust sector for trade policy. The Foreign Trade policy 2004-09 and the
Union Budget for 2003-04 have sought to promote export of services through
access to service providers to duty-free imports, advance licences,
venture capital funds and by formulation of specific action plans for the
services sector. The Foreign Trade Policy 2004-09 has announced the
setting up of a Services Export Promotion Council to snap opportunities
for services in important markets and to develop strategic market access
programmes including brand building. This would be in co-ordination with
sectoral players and recognised nodal bodies of the service industry.
Foreign trade policy also announced ‘Served from
|
Served
From |
|
|
Objective |
The
objective is to accelerate the growth in export of services so as
to create unique ‘Served From India’ brand, instantly
recognized and respected the world over. |
|
Entitlement Hotels
& Restaurants |
All
Service providers (other than hotels and restaurants) will be
entitled to duty credit equivalent to 10 per cent of the foreign
exchange earned by them in the preceding financial year. Hotels
of one-star and above (including managed hotels and heritage
hotels) approved by the Department of Tourism, and other Service
providers in the tourism sector registered with the Department of
Tourism, will be entitled to duty credit equivalent to 5 per cent
of the foreign exchange earned by them in the preceding financial
year. Stand-alone restaurants will be entitled to duty credit
equivalent to 20 per cent. |
|
Healthcare
& Education |
In
order to enable healthcare and educational institutions to have
world-class state-of-the-art infrastructure, service providers in
these sectors shall, as for other service sectors, be entitled to
duty credit equivalent to 10 per cent of the foreign exchange
earned by them in the previous financial year. |
|
Software |
In
order to boost software exports, the government has taken up
special initiatives and has set up the Electronics
and Computer Software Export Promotion Council (ESC) - an
autonomous organisation under the Ministry of Information
Technology, Government of India. It is the nodal agency to promote
the electronics and computer Software trade with |
In addition, the government is also planning to promote the establishment of ‘Common Facility Centres’ for use by home-based service providers, particularly in areas like engineering & architectural design, multi-media operations, software developers etc. in state and district-level towns, to encourage home-based professionals into the services export arena.
In the latest Annual Supplement to Foreign Trade Policy 2004-09, released on the 7th April 2006, a number of features have been added in the Served from India Scheme to meet the requirements of service exports. They are:
-
Service exports in Indian Rupees, which are otherwise considered as having been paid for in free foreign exchange by RBI, will now qualify for benefits under the Served from India Scheme. In addition, the foreign exchange earned through International Credit Cards and other instruments as permitted by RBI for rendering of service by the service providers shall be taken into account for the purposes of computation of entitlement under the Scheme.
-
Benefits of the Scheme earned by one service provider of a Group company can now be utilised by other service providers of the same Group Company including managed hotels. The measure aims at supporting the Group service companies not earning foreign exchange in getting access to the international quality products at competitive price and providing services of international standards. This new initiative allows transfer of both the scrip and the imported input to the Group Service Company, whereas the earlier provision allowed transfer of imported material only.
-
Stand-alone restaurants will now be eligible for benefits under Served from India Scheme at 10 per cent of FOB value of exports (instead of the earlier 20 per cent).
GATS:
Strategies for
Since
1995, international trade in services has moved into centre-stage in
international trade policy negotiations with the first set of
international rules for trade in service being brought into force under
the General Agreement on Trade in Services (GATS) of the World Trade
Organisation (WTO). Negotiations commenced on January 1, 2004 which are
based on request-offer approach.
Given
Conclusion
The
rising importance of trade in services calls for exploiting competitive
advantage that
End-Notes
-
The balance of payments accounting is carried under two heads, namely current account and capital account. Transactions relating to goods, services, income and current transfers constitute the current account. This current account is again classified into two broad categories: merchandise and invisibles and services form a major part of invisible transactions.
-
There are four ways or ‘modes’ of delivering or trading a service: Mode 1 is where services are supplied from one country to another (for example international telephone calls), officially known as “cross-border supply”; Mode 2 is where consumer or firms make use of a service in another country (for example tourism) officially known as “consumption abroad”; Mode 3 is where a foreign company sets up subsidiaries or branches to provide services in another country (for example foreign banks setting up operations in a country), officially known as “commercial presence” and Mode 4 is where individuals travel from their own country to supply services in another country (for example fashion models, architects or consultants), officially known as “movement of natural persons”.
* This note is prepared by Gauri A Ranade and Abhilasha Maheshwari.
Highlights of Current Economic Scene
AGRICULTURE
The
central government has indicated the plans to import additional 1.5
million tonnes of wheat. The additional imports are meant to strengthen
food stocks in the severely depleted central grain pool owing to the
downward revision of wheat estimates to 73.1 million tonnes and fears of
damage to the crop due to unusual rise in temperatures in February
following untimely rains. The fresh order would push up total wheat
imports to 2.0 million tonnes. The farmers have protested this move since
it has been taken at the beginning of the marketing season for wheat,
which by improving supply condition, is expected to restrain the possible
higher returns to the producers. Wheat procurement has begun on fresh
arrival of the new crop from major wheat producing states like Punjab,
Haryana, Madhya Pradesh, Uttar Pradesh and
After
hitting Maharashtra and Gujarat, bird flu has now been detected in the
Ichhapur town of
The
poultry industry in Andhra Pradesh has suffered a loss of Rs 3,500 crore
in 6 weeks on account of fear factor of spread of avian flu since its
outbreak in the country. While the layers (eggs) segment has incurred a
loss of Rs 2,000 crore, the broilers (meat) has lost the business worth Rs
1,500 crore. As per All India Broiler Farmers’ marketing Co-operative
Ltd, consumption of broiler has fallen drastically from 8 crore broiler
per day to about 8 lakh birds per day. The farmers have undertaken
deliberate molting of one-fourth of six crore layers. There have been
reports of poultry farmers in
The central government has allowed the sugar mills to export sugar from marketable surplus instead of using levy quota for this purpose. The millers have to undertake sugar exports to fulfill their re-export obligation on previous year’s raw sugar import. However, the move has been taken in the wake of expected higher sugar production to 182-183 lakh tonnes for 2005-06 against 121-121 lakh tonnes in 2004-05, which would likely generate surplus over domestic consumption.
In
order to control the pepper imports from
The
country is expected to export 50,000 tonne of sugar to
The Commerce Ministry is considering the proposal to set up a special purpose vehicle for market intervention in the tobacco market to address the frequent problem of price surplus. The central government and the Tobacco Board would also help the Ministry in making the switchover as smooth as possible.
INDUSTRY
Overall
The industry ministry has sought Rs 956 crore over a period of five years for implementing the national manufacturing initiative. The funds will be used for 10 areas identified as priority action areas by the National Manufacturing Competitiveness Council (NMCC), including a national programme on application of lean manufacturing, technical upgradation support to small and medium enterprises (SMEs), entrepreneurial and management support to SMEs, a national campaign for an intellectual property rights regime and promotion of information & communication technology. The Planning Commission, which has informally indicated its willingness, has been asked to allocate a portion - Rs 150 crore - of the entire amount in the ministry’s annual plan for 2006-07.
FMCG
Spurred by high rural demand and retail sales, the fast-moving consumer goods (FMCG) sector has posted 10.6 per cent growth year on year in February 2006, the highest in the past five years, according to data provided by market research agency AC Nielsen. The rise does not come on a low base since the sales growth in February 2005 had been 8.1 per cent year on year. Also, the growth has been broad-based with all the top 10 categories growing, the only exception being packaged tea.
Automobiles
The sub-committee on human resources development, constituted under the automobile mission document taskforce, has projected that employment in the auto component industry will rise 10-fold to 2.55 million by 2015. In a report submitted to the ministry of heavy industry, it has been commented that while an increase in efficiency levels and more automation has seen employment stable over the past 4-5 years, increasing incremental investment and green field projects will see demand for skilled personnel rising.
Chemicals
The
department of fertilisers (DoF) has proposed a 10 per cent increase in
re-assessed urea production capacity under the new pricing scheme
beginning April 1, 2006. The units undertaking de-bottlenecking or
revamping will, however, be allowed to retain energy efficiency gains and
it will not be mopped up for a revision in the pre-set energy norms for
the stage-III of the scheme. Approval will be given for the expansion
projects subject to the condition that the additional production beyond
the present reassessed capacity shall be eligible for subsidy by the
government only in case it is required to be sold to the farmers under the
extended subsidy scheme. In case the government does not require the whole
or part of the additional quantity for agricultural uses, the units will
be free for export or any other industrial use. The move is expected to
add an additional capacity of 7 lakh tonnes of urea annually in a cost
effective manner with use of natural gas or LNG. Several companies
including Tata Chemicals, Indo-Gulf, Iffco and Chambal Fertilizers have
submitted revamp proposals. Last year, the country has imported 9 lakh
tonnes of urea.![]()
INFRASTRUCTURE
Overall
Infrastructure growth has bounced back to 5.6 per cent in February 2006 from a meagre 0.8 per cent in the same month last year, largely on the back of a surge in power-generation and coal and cement production. The sectors that have shown a dip in growth include steel and crude oil. The other four sectors - oil refining, coal, cement and power – have registered improved production levels during the month. However, the cumulative growth during April-February 2005-06 has been 4.5 per cent as against 5.8 per cent in the corresponding period last fiscal year.
Energy
As per a report by KPMG, the potential for private sector investment in the country’s energy sector could be around $9-10 billion over the next 5-6 years. Of this, power transmission alone could attract as much as $ 4.5 billion, with energy management and investments in coal mining attracting up to $3 billion and $2 billion, respectively. The coal sector, the report says, presents an immediate opportunity for private investors as reserves in excess of 1,000 million tonnes are being allotted for captive mining. The gas sector too offers opportunities, as the demand side of auto CNG and piped gas are together expected to account for 7 per cent of the total demand in the next five years. In the power sector, there are emerging opportunities in generation as well as transmission and distribution. In the renewable energy sector, there is potential in small hydro and wind energy, where the government is targeting an additional capacity of 10,000 MW by 2012. On the hydro front, opportunities lie in the 45,000 Mw capacity addition targeted in the next 10 years.
Power
The Centre has launched massive renovation, modernisation and uprating (RM&U) of hydro power projects across the country to augment the hydro generation and improve the availability of existing projects. For the Eleventh Plan (2007-12), it has identified 59 hydro projects under RM&U with an installed capacity of 10,325.40 MW at an estimated cost of Rs 3,116.40 crore, which would accrue a benefit of 5,461.18 MW. As per reports, the cost per MW of a new hydro project works out to be around Rs 4-5 crore, whereas the cost per MW of capacity addition through uprating and life extension uprating of old hydro project works to about 20 per cent of the amount. Further, RM&U of a hydro project can be completed in one to three years depending on the scope of works as compared to a gestation period of five to six years for new hydro projects.
Coal
The government has increased coal linkages for the core sectors, namely power, steel and cement, by about 5 million tonnes (mt) for the first quarter of next fiscal year ending June 30, 2006 i.e. 91.2 million tonnes of coal at notified prices. Of the approved linkage, the power sector would be given the bulk of coal to the tune of 78.66 mt, about 3 mt more than the linkage approved for the same period of current fiscal year.
Railways
The railway ministry has finalised an investment strategy giving highest priority to route-wise works on high-density network, in view of the announcement made by railway minister that all pending project works would be completed in the next three years. A number of initiatives have been taken for generation of additional resources through specific funding for national projects, funding from defence ministry, public-private partnership and non-budgetary initiatives for ‘National Rail Vikas Yojana’ to complete these projects.
INFLATION
The annual point-to-point inflation rate based on wholesale price index (WPI) has gone down to 4.06 per cent for the week ended March 18, 2006 from 4.28 per cent during the previous week. The inflation rate was at 5.45 per cent in the corresponding week last year.
The WPI in the week under review has declined by 0.1 per cent to 197.4 from 197.5 in the previous week (Base: 1993-94=100). The index of primary articles’ group (weight 22.02 per cent) has declined considerably by 0.6 per cent to 192 from the previous week’s level of 193.1, due to a decline by 0.5 per cent and 0.9 per cent in the price index of food articles and non-food articles, respectively. The index of ‘food articles’ has declined to 193.8 from 194.7 in the previous week, mainly due to decline in the prices of poultry chicken, tea, moong, fish-inland, fruits and vegetables, eggs and pork. Similarly, the index of non-food articles has declined to 174.6 from 176.1 in the earlier week, due to the decline in the prices of fodder, raw cotton, raw rubber, safflower and copra. The index of ‘fuel, power, light and lubricants’ group (weight 14.23 per cent) has risen considerably by 0.5 per cent to 316.3 from 314.7 in the previous week, due to the higher prices of furnace oil, bitumen and naphtha. The index of ‘manufactured products’ group constituting the maximum of 63.7 per cent of total weight, has remained unchanged at the previous week’s level of 172.8.
The latest final index of WPI for the week ended January 21, 2006 has been revised downwards; as a result both, the absolute index and the implied inflation rate stood at 196.5 and 4.24 per cent as against their provisional levels of 197 and 4.51 per cent, respectively.
The rate of inflation has generally remained contained in the range of 4 to 4.5 per cent in last couple of months. According to the Economic Survey 2005-06, the annual point-to-point inflation rate is expected to be around 5 per cent at the end of March 2006.
BANKING
The
Reserve Bank of India (RBI) is likely to reduce the mandatory cash reserve
ratio for public sector banks from the current 5 per cent to 4 per cent to
ease the liquidity position. A 100 basis points cut would release Rs
20,000 crore into the system. (P.1, TFE, 28/3/2006).
The
RBI has liberalised rules governing coporate guarantees and disinvestment.
It has also eased the regulatory regime for overseas investment by
proprietary concerns. Under the new regime, Indian corporates can offer
all forms of guarantees subject to overseas investment cap of 200 per cent
of networth. At present, only promoter companies are allowed to offer
guarantees on behalf of their wholly-owned subsidiaries and joint
ventures. All other guarantees require a prior RBI approval.
Yielding
to one of the key demands of the banking community, the RBI has hiked the
interest rate ceiling on FCNR(B) deposits by 25 basis points. In the
April-December period, the outstanding FCNR(B) deposits stood at $11.6
billion. The move follows a meeting of senior bankers with RBI governor in
which they asked for a cut in the cash reserve ratio, unwinding of market
stabilization securities and deregulation of expatriate deposits to ease a
liquidity squeeze in the banking system. The decision is expected to
further bolster banks’ deposit mobilization programme and will impart
some liquidity into the system.
Following
the introduction of norms for issuance of perpetual debt instruments by
RBI in January 2006, a large number of banks are increasingly tapping the
hybrid capital route to raise the fresh capital. The banking industry
plans to raise close to Rs 3,000 crore through issuance of perpetual debt
instruments in a couple of months. Among the state-run banks, UCO Bank was
the first bank to raise Rs 200 crore through hybrid upper Tier II bonds
carrying a coupon of 8.75 per cent.
RBI
has permitted transfer/trading in power bonds maturing on October 1, 2010
and April 1, 2011, issued by various states to central public sector
undertakings in terms of Tripartie Agreement among 27 state governments,
ministry of power, government of India and the RBI, under One Time
Settlement Scheme for dues of State Electricity Bonds.
PUBLIC
FINANCE
The revised estimate (RE) 2005-06 for net tax revenue is at Rs 2,74,139 crore which is 0.25 per cent higher than the budget estimate (BE) of Rs 2,73,466 crore. The actual net tax revenue collection during April-February 2005-06 is at Rs 2,07,847 crore which is 75.8 per cent of RE 2005-06.
The revised estimate (RE) for the total receipts is Rs 3,62,530 crore, which is 0.18 per cent lower than the budget estimate (BE) of Rs 3,63,200 crore for 2005-06. The actual total receipts received during April-February 2005-06 are at Rs 2,79,702 crore which is 77.2 per cent of RE.
The RE for total expenditure is at Rs 5,08,705 crore which is 1.09 per cent lower than the BE of Rs 5,14,344 crore for 2005-06. The total expenditure during April-February 2005-06 is Rs 4,11,922 crore which is 81.0 per cent of RE.
The RE for fiscal deficit is at Rs 1,46,175 crore which is lower by 3.28 per cent as compared to BE of Rs 1,51,144 crore 2005-06. During April-February 2005-06 the actual fiscal deficit is Rs 1,32,220 crore which is 90.5 per cent of the RE.
The RE 2005-06 for revenue deficit is at Rs 91,821 crore which is lower by 3.66 per cent as compared to Rs 95,312 crore BE 2005-06. However, actual revenue deficit during April-February 2005-06 is at Rs 98,652 crore which is 107.4 per cent of RE 2005-06. The revenue deficit during April-February 2004-05 is 108.8 per cent of the RE 2004-05.
FINANCIAL
MARKET
Capital
Markets
Primary
Market
Sun TV will be tapping the market on April 3, 2006 with its public issue of 6,889,000 equity shares, offering a price band of Rs 730 to Rs 875 per equity share. The issue would constitute 10 per cent of the fully diluted post issue paid-up capital of the company. The issue closes on April 7,2006.
Opto Circuits (India) Limited plans to tap the market on March 31 with their public issue of 40 lakh equity shares at a price band of Rs 240 to Rs 270 per equity share, the issue would constitute 12.98 per cent of the fully diluted post issue paid up capital of the company. The issue closes on April 5,2006.
R Systems International Limited tapped the market on March 27 with its public issue of 44 lakh equity shares at a price band of Rs 210 to Rs 250 per share. The issue closes on March 31.
Secondary
Market
The
market retained its bullishness during the week, supported by firm global
markets trends, short covering in the derivative market as well as the
sustained strong FIIs inflows in the market. During the week, the sensex
surged by 329.66 points to settle at 11279.96 points and S&P CNX Nifty
also rose by 122.75 points to close the week at 3402.55 points. Among the
sectoral indices, all the indices closed in the positive territory except
BSE CD index, which registered a decline of 0.72 per cent at 3212.33
points. BSE METAL registered the highest gain of 8.39 per cent as it
closed at 8869.91 points, followed by BSE FMC at 5.13 per cent at 2211.45
points.
Sebi
has, on March 20, for the first time, decided to entrust the stock
exchanges with the responsibility of registration of sub-broker. The
regulator, however, will continue to monitor the registration process and
retain the final authority of according the approval.
On
March 27, the combined turnover of the BSE and NSE was pegged at Rs
17,588.89 crore, with NSE alone reporting a record turnover of Rs
11,395.99 crore in cash segment. This is for the first time in the history
of NSE that the turnover has breached the Rs 11,000 crore mark. Meanwhile,
the total turnover of cash and derivatives segment stood at Rs 55,264.74
crore.
The
net FII investment in the equity for the month of March 2006 stood at Rs
6688.80 crore with purchases worth Rs 52941.10 crore and sales of Rs
46252.20 crore, while in the derivative market in the futures segment
their net position stood at Rs 983.12 crore and in options it stood at
585.47 crore. Meanwhile, the mutual funds have also being net buyers in
the month of March to the extent of Rs 2624.03 crore with purchases worth
Rs 33904.16 crore and sales of Rs 31280.13 crore.
Derivatives
The total turnover of NSE’s F&O segment for the week ending March 31 stood at Rs 191358 crore; as usual the futures continued to contribute the bulk of the trading with total turnover of Rs 174806 crore, while the options total turnover stood at Rs 16552 crore.
Government
Securities Market
Primary
Market
The RBI has mopped up Rs 6000.26 crore and Rs 1750 crore through 91-day treasury and 364-day treasury bills, respectively. The cut-off yield for 91-day treasury bill and 364-day treasury bill were 6.1081 per cent and 6.4232 per cent, respectively.
Meanwhile, the RBI conducted the auctions of State Development Loan (SDL), 2016 for nine states for an aggregate amount of Rs 1820.62 crore. The cut-off of SDL 2016 for Assam, Jammu and Kashmir was 7.75 per cent, for Punjab and Tamil Nadu was 7.79 per cent, for Manipur, Meghalaya, Mizoram, Nagaland and Uttaranchal were 7.74 per cent, 7.70 per cent, 7.71 per cent, 7.69 per cent and 7.72 per cent, respectively.
Secondary
Market
During the week, the call rates ended firm at 6.70-6.90 per cent higher from their last week’s close of 6.50-6.70 per cent. The concern regarding interest rates and firming international crude oil prices also dampened the market sentiments. During the week, the amount placed under the repo facility of RBI has averaged to Rs 7312 crore, against Rs 4348 crore in the previous week. Meanwhile, the average daily subscriptions at the reverse repo auction rose to Rs 7435 crore from Rs 571 crore in the previous week. The RBI, in order to facilitate funds management by banks on account of the year-close on March 31 falling on a reporting Friday, conducted an additional liquidity adjustment facility.
Bond
Market
The
RBI is likely to revise its guidelines on hybrid instruments, with a view
to enabling scheduled commercial banks to raise additional capital.
Foreign
Exchange Market
In
the forex market, irrespective of sustained dollar buying form public
sector banks and suspected RBI intervention the rupee stood marginally
firm at Rs 44.62 per dollar from Rs 44.66 per dollar in the previous week.
However, arbitrage opportunities at the NDF front and the further scope of
credit tightening signaled by the FOMC, which raised its interest by a
quarter percentage to 4.75 per cent on March 29 saw the rupee weakening to
two and a half month lows at around Rs 44.75 per dollar. However, the
rally in the domestic stock market supported the rupee movement. In the
forward premia segment, the premia moved in a tight range and remained
volatile as it tracked the liquidity conditions in the money market.
Commodities
Futures Derivatives
MCX
has, on March 28, launched futures trading in Arecanut of white variety.
Initially May and June contract will be offered for the trading and the
contract lot size will be 1 metric tonne, the contract will expire on 15th
of every month.
The
domestic bullion prices, on March 30, scaled to new records after prices
in
MCX,
on March 30, has signed a memorandum of understanding (MoU) with Bursa
Malaysia Derivative Berhad for trading in crude palm oil contracts on the
Malaysian Exchange. The contracts that would be traded would be rupee
denominated, which would enable traders to hedge themselves against price
volatility. Both the exchanges will also work jointly towards market
development, risk hedging and domain knowledge.
CREDIT
RATING
Crisil has assigned a ‘P1’ rating to Dorf Ketal Chemicals (I) Private Limited’s (Dorf Ketal’s) Rs 150 million commercial paper programme. The rating derives strength from Dorf Ketal’s significant domestic and global presence in its niche product segments, strong competitive position driven by research and development and customized products and services and comfortable financial risk profile.
Crisil has assigned ‘AAA’ rating to Corporation Bank’s Rs 3 billion lower tier II bonds. The agency has also reaffirmed the ‘ AAA’, ‘FAAA’ and ‘P1+’ rating assigned earlier to the bank’s Rs 2 billion lower tier II bonds, fixed deposit programme and certificates of deposits programme, respectively. The assigned rating reflects the bank’s sound capital adequacy, superior asset quality and comfortable earnings level.
Crisil has reaffirmed the ‘P1+’ rating assigned to Navneet Publication’s Rs 500 million short-term debt programmes (enhanced from Rs 300 million). The rating continues to reflect the company’s sustained comfortable financial risk profile marked by healthy cash accruals.
Crisil has reaffirmed the ‘P1+’rating assigned to Hyundai Motor India Limited’s Rs 1 billion short-term debt programmes. The reaffirmation reflects the company’s established presence in the B and C segments of the domestic passenger car industry, status as the global sourcing hub for small cars, strong financial risk profile and efficient cost structure.
Crisil
has reaffirmed the ‘AAA’ and ‘P1+’ ratings assigned to GE Capital
Services (I) Limited’s Rs 30 billion non-convertible debentures
programme and Rs8.5 billion short-term debt programmes, respectively.
The reaffirmation is primarily based on the fact that GE Capital Services
India (GECSI) is owned by the General Electric group (GE) through GE
Capital Corporation (GECC) and on the strategic importance of the
commercial finance business for GE.
Crisil has assigned ‘AA- ‘ rating to the Balkrishna Industries’s Rs 100 million non-convertible debenture programme. The assigned rating reflects the company’s strong financial risk profile and business growth driven by capacity expansion and high operating efficiency.
Icra
has assigned ‘LAAA’ rating with stable outlook to the proposed Rs 15
billion long-term bond programme of EXIM Bank. The rating take into consideration the strategic role that EXIM plays in
meeting the government’s policy objectives of promoting bilateral trade
and exports of Indian products and services, besides the bank’s
favourable capital adequacy and capitalisation levels, improving asset
quality indicators and comfortable liquidity position also supports the
rating.
Icra
has assigned ‘A1+’ rating to the Rs 30 billion (enhanced from Rs 20
billion) certificate of deposit programme of State Bank of Patiala (SBP).
The agency has also reaffirmed the ‘LAAA’
rating to the tier II bonds and ‘MAAA’ rating to term deposit
programme of the bank. The rating reaffirmation factors in SBP’s strong
franchise value in its areas of operations enabling a stable deposit base
and sustained market position demonstrated in the growing credit
portfolio. The rating also factors in SBP’s stable core operating
profitability supported by low overhead expenses, comfortable capital
adequacy, solvency and ability to maintain comfortable liquidity.
Icra
has assigned a ‘ LAA’ rating to the Rs 3 billion perpetual bonds of
Indian Overseas Bank (IOB). The rating
assigned to the perpetual bonds reflects the specific features of these
instruments wherein the debt servicing is additionally linked to meeting
the regulatory norms on capitalization and reported profitability.
Icra
has assigned an ‘LAA’ rating to the fresh Rs 3 billion tier II bond
programme of United Bank of India (UBI). The agency has also assigned and
‘A1+’ rating to the Rs. 10 billion certificate of deposit programme of
UBI.
Icra
has assigned an ‘LAAA’ rating with stable outlook to the Rs. 150
billion borrowing programme for 2006-07 of Housing Development Finance
Corporation Limited (HDFC). The ratings reflect HDFC’s dominant market
position in the housing finance (HF) industry, competitive operating cost
structure, improving profitability despite intense competition, sound
asset quality, well-diversified resource base and comfortable
capitalisation levels.
Fitch
Ratings has assigned a National Long-term rating of ‘A (
Care
has assigned ‘AAA’ rating to the umbrella borrowing programme for FY06
and FY07 of National Bank for Agriculture and Rural Development (NABARD)
aggregating to Rs.2000 crore for maturities upto 10 years. Also, the
agency has retained the ‘AAA’ rating to various debt instruments of
NABARD.
CORPORATE
SECTOR
Hetero Drugs, the Hyderabad based pharmaceutical company, has bought over its joint venture partners entire holding in Lyka Hetero Healthcare for an undisclosed amount. Lyka was a 51:49 joint venture between the N I Gandhi promoted Lyka Labs and Hetero Drugs.
Ranbaxy
Laboratories has acquired 96.7 per cent of
L.N. Mittal has acquired 8.2 per cent shares in Indiabulls Credit Services, the majority owned subsidiary of IndiaBulls Financial Services, for Rs 90 crore.
Bajaj Auto has scales up its share in Mukand Limited by 2.14per cent through open market operations.
Zee Telefilms Limited, media major, has announced a restructuring of its broadcasting business to create three independent entities by hiving off its cable distribution arm, Siti Cable (the country’s biggest cable network), its news operations (six existing channels), and its DTH business- Dish TV.
Wipro
Infotech has secured a Rs 360 crore information technology outsourcing
contract from HDFC Bank. The contract spread over 10 years is
Western
India Shipyard has secured major contract from Adani Group compay PMC
Projects (
Utility vehicle maker Mahindra and Mahindra is planning to set up a motorcycle assembly plant at Haridwar in Uttaranchal at an estimated investment of Rs 300-400 crore. The 30,000 unit capacity plant is expected to start marketing 100cc and 125/150cc bikes by 2008.
Low cost airlines SpiceJet has registered a 60 per cent rise in its net sales to Rs 130.7 crore in the quarter ended February 2006 over the previous quarter. The company has reported a net profit of Rs 4.3 crore in the quarter ended February 2006, as against a net loss of Rs 21.36 in the previous quarter.
Pfizer Limited has posted 84 per cent rise in the net profit for the quarter ended February 2006 to Rs 24.8 crore over the same period previous year.
EXTERNAL
SECTOR
LABOUR
According
to the Outcome Budget (2006-07) tabled in the parliament on March 21, the
National Rural Employment Guarantee Scheme (NREGS) is expected to provide
100 days of guaranteed wage employment to 1.16 crore rural households,
generating 116.12 crore mandays during 2006-07. While Rs 10,556 crore (91
per cent) would be made available by the centre for providing wage
employment guarantee, the states would contribute the remaining Rs 1,056
crore. The Outcome Budget also mentions that the outcomes under the NREGA
(An Act enabling NREGS) would be ‘the creation of durable assets and
strengthening the livelihood resource base of the rural poor’. It added
that this would take at least 3-4 years before this outcome could be
materialised. Even in the case
of Integrated Child Development Services (ICDS), which seeks
to provide an integrated package of health, nutrition and educational
services to children up to six years of age, pregnant women and nursing
mothers, the Outcome Budget mentions that the impact would be assessed
through an independent agency at the end of 3 to 5 years. One of the
quantifiable outputs under the ICDS for 2006-07 is to operationalise 5,635
projects. Similarly, the Sarva Shiksha Abhiyana (SSA) is targeted for
enrollment of 100 million children in the age group of 6-14 years in
2006-07. An additional five lakh classrooms will be also created taking
the total number of classrooms to 34 lakh in 2006-07. Similarly, as many
as 1.5 lakh teachers would be recruited, taking the total number of
teachers to 42 lakh till the end of 2006-07.
TELECOM
The
department of telecom (DoT) has released new guidelines with regard to
increasing the limit of spectrum for GSM and CDMA operators on the basis
of their subscriber base respectively. The move comes as a major boost to
the mobile industry, which is adding as many as 5 million subscribers per
month. While the total spectrum was capped at 10 Mhz for GSM and 5 Mhz for
CDMA players, it has now been raised to 15 Mhz for GSM and 7.5 Mhz for
CDMA for 21 lakh subscribers each. According to new criteria, a GSM
operator will get spectrum beyond 10 Mhz in two tranches – from 10 Mhz
to 12.4 Mhz (when it crosses 10 lakh subscribers) and 12.4 Mhz to 15 Mhz
(when it crosses 16 lakh subscribers). The CDMA operators will get beyond
5 Mhz to 6.25 Mhz and then to 7.25 Mhz. The new criteria comes into effect
immediately. It has, however, not taken into account the demand of CDMA
operators that equal spectrum be allotted to GSM and CDMA operators for
the same number of subscribers. For
|
Macroeconomic Indicators |
|
Table
1 : Index Numbers of Industrial Production (1993-94 =100) |
|
Table
2 : Production in Infrastructure Industries (Physical Output Series) |
| Table 3: Procurment, Offtake and Stock of foodgrains |
|
Table
4: Index Numbers of Wholesale Prices (1993-94 = 100) |
|
Table
5 : Cost of Living Indices |
|
Table
6 : Budgetary Position of Government of India |
|
Table
7 : Government Borrowing Programmes and Performance |
|
Table
8 : Scheduled Commercial Banks -
Business |
|
Table
9 : Money Stock : components and Sources |
|
Table 10 : Reserve Money : Components and Sources |
|
Table
11 : Average Daily Turnover in Call Money Market |
|
Table
12 : Assistance Sanctioned and Disbursed by All-India Financial
Institutions |
|
Table
13 : Capital Market |
|
Table
14 : Foreign Trade |
|
Table 15 : India's Overall Balance of Payments |
|
Table
16 : Foreign Investment Inflows |
| Table 17 : Foreign Collaboration Approvals (Route-Wise) |
| Table 18 : Year-Wise (Route-Wise) Actual Inflows of Foreign Direct Investment (FDI/NRI) |
|
Table
19 : NRI Deposits - Outstandings |
|
Table
20 : Foreign Exchange Reserves |
|
Table 21 : Indices REER and NEER of the Indian Rupee |
|
Table
22 : Turnover in Foreign Exchange Market |
| Table 23 : India's Template on International Reserves and Foreign Currency Liquidity [As reported under the IMFs special data dissemination standards (SDDS) |
| Table 24 : Settlement Volume and Netting Factor for Government Securities Transactions Settled at CCIL - Monthly, Quarterly and Annual Basis. |
| Table 25 : Inter-Catasegory Distribution of All Types of Trade in Government Securities Settled at CCIL (With Market Share in Respective Trade Types) |
| Table 26 : Category-wise Market Share in Settlement Volume of Government Securities Transactions (in Per Cent) |
| Table 27 : Settlement Volume and Netting Factor for Total Forex Transactions Settled at CCIL - Monthly, Quarterly and Annual Basis. |
| Table 28 : Inter-Category Distribution of Total Foreign Exchange Transactions Settled at CCIL (With Market Share in Respective Trade Types) |
|
Memorandum Items |
*These statistics and the accompanying review are a product arising from the work undertaken under the joint ICICI research centre.org-EPWRF Data Base Project.
We will be grateful if you could kindly send us your feed back at epwrf@vsnl.com