Current Economic Statistics and Review For the
Week
Ended April 22, 2006
Theme
of the week:
Organic Farming: Turning to Nature for Healthier Growth**
Introduction
Inception
of agricultural revolution was marked with the invention of a seed drill
and application of manure using a horse-drawn hoe in
Modern
farming techniques (use of fertlisers, pesticides, high yielding variety
seeds, etc.), which resulted in the ‘Green Revolution’, have been a
cornerstone of agriculture sector’s achievements in
Concept
Organic
agriculture is one among the broad spectrum of production methods, that
focuses on ecological tenets as the basis for crop production and animal
husbandry. The philosophy
behind the concept of organic farming is to feed the soil rather than the
crops to maintain soil health and it is a means of giving back to the
nature what has been taken from it. Very often it is mistakenly considered
as synonymous to traditional agriculture or sustainable agriculture or
method of using organic manures instead of synthetic fertilizers /
pesticides for crop production and protection. According to one of the
definitions, the term "organic" is best thought of as
referring not to the type of inputs used, but to the concept of the farm
as an organism, in which all the components - the soil minerals, organic
matter, microorganisms, insects, plants, animal and humans - interact to
create coherent, self-regulating and stable whole. Reliance on external
inputs, whether chemical or organic, is a reduced as far as possible.
Organic farming is (w) holistic production system[1].
The Codex Alimentarius Commission, a joint body of Food and Agriculture
Organisation of the United Nations (FAO) and World Health Organisation
(WHO) defines “organic agriculture as holistic food production
management system, which promotes and enhances agro-ecosystem health,
including biodiversity, biological cycles and soil biological activity.
It emphasizes the use of management practices in preference to the
use of off-farm inputs, taking into account that regional conditions
require locally adapted systems. This
is accomplished by using, where possible, agronomic, biological and
mechanical methods, as opposed to using synthetic materials, to fulfill
any specific function within the system”. The term ‘organic’
reveals that the products follow the defined standard of production and
handling and are certified by a duly constituted certification body or
authority. ‘The organic label is, therefore, a process claim rather
than a product claim. It should not necessarily be interpreted that the
food-products from organic farming are healthier, safer or all natural. It
simply means that the products follow the defined standard of production
and handling, although surveys indicate that the consumer conducts organic
label as an indication of purity and careful handlings.’ [P. Ramesh et
al, (2005), Pg: 562]
Thus, the promotion of soil fertility, biodiversity (e.g. native flora and fauna), locally- adapted production methods and the minimal usage of chemical inputs, lie at the core of organic agriculture. Such methods and the cultivation of diverse crops stabilise the delicate eco-systems in the tropics and reduces drought sensitivity by improving water holding capacity of soil and help in pest and crop disease management. Organic production lowers the risk of declining yield, stabilises returns, and therefore, enhances food security of small farmer families. The impact of organic agriculture on natural resources favours interactions within the agro-ecosystem, which are vital for both agricultural production and nature conservation through waste recycling, carbon sequestration and nutrient cycling.
Organic
Farming: Global Scenario
According
to the latest statistics provided by 'The World of Organic Agriculture –
Statistics and Emerging Trends 2006'[2],
organic agriculture has been practiced in approximately 120 countries
around the world, with more than 31 million hectares of farmland being
under organic management in 2006.
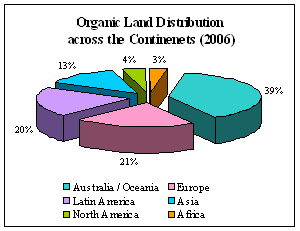 The coverage has exceeded by around five
million hectares as compared with the previous year. Besides, it is
believed that uncertified organic farming is also in practice in more
number of countries. In terms
of organic land,
The coverage has exceeded by around five
million hectares as compared with the previous year. Besides, it is
believed that uncertified organic farming is also in practice in more
number of countries. In terms
of organic land,
All
the Latin American countries practice organic farming to some extent or
the other; however,
European
Union (EU):
Among
the EU countries,
Distinctive
feature of this market is provision of a guarantee to consumers that those
organic products using the labelling imply that specific practice has been
followed during the production of those products. The study has estimated
the sales of organic food and drink at US $ 14.5 billion in 2005. With the
consumer demand rising continuously, the region is expected to attract
maximum revenue in the global organic food market.
The
principal countries involved in organic production are
An
important factor in African continent that has encouraged the organic
production is the demand for organic products in the industrialised
countries. Another motivation is the maintenance and building of soil
fertility on land threatened by degradation and erosion. Market for
organic produce in the African continent is very small except in
Table
1: Overview of Global Organic Market
|
|||||||
|
Value
of Organic Food Sales (US $ million) |
|||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
8000 |
2100 |
1000 |
1000 |
850 |
450 |
||
|
Global
Market (US $ billion) |
|||||||
|
2000 |
2001 |
2002 |
2003 |
||||
|
17 |
25 |
26 |
31 (E) |
||||
|
(E):
Expected Source: No 1 under references |
|||||||
Organic
Farming: The Indian Context
The
roots of organic agriculture in
Considering
the natural potential available for organic production in the country and
its growing consumer preference for the organic products at the global
level, the government has taken various initiatives to boost organic
farming in the country. To state a few of them :
*
The Planning
Commission constituted (2000) a steering group on agriculture who
identified organic farming as a national challenge and suggested that it
to be taken in the form of a project as a major thrust area under the 10th
five year plan. Accordingly, Ministry of Agriculture has formulated a
scheme, which envisages the setting up of a National Institute of Organic
Farming (NIOF) which would be responsible for the promotion of organic
farming, setting standards wherever necessary, expanding the regulatory
mechanism to cover the requirements of small and marginal farmers, etc.
*
Ministry of
Commerce has launched a ‘National Programme for Organic Production (NPOP)’
in May 2001 for export purpose and has established a regulatory mechanism,
which covers fixing of standards for organic cultivation, accreditation of
certification agencies and inspection etc. NPOP standard has got
equivalency with the standard of EU commission in 2005 and now Indian
standard is acceptable in European Countries.
In
*
Various
government agencies like APEDA, Export-Import Bank are involved in
promoting organic products by participating in international conferences.
APEDA has identified exclusive Agri-Export Zones (AEZ) for organic produce
in some part of the country, such as organic pineapple in Tripura.![]()
Market
Situation
The
market activities are concentrated around exports of organic products
rather than domestic consumption. Major domestic markets consist of
metropolitan cities like Mumbai,
|
Table
2: |
|||
|
Area under certified (in million hectares) |
2.5 |
Total certified product (in metric tonnes) |
115,238 |
|
Total project certified |
332 |
Number of processing units |
158 |
|
Accredited inspection and certifying agencies |
11 |
Number of products exported |
35 |
|
All
|
6,472 |
Premium collected against organic export (tentative) |
Rs. 80-90 crore |
|
States involved in organic export (in metric tonnes) |
|||
|
Kerala |
1232 |
|
937 |
|
|
541 |
Himachal Pradesh |
521 |
|
Karnataka |
476 |
Tamil Nadu |
471 |
|
|
375 |
|
|
|
Source:
No
(1) under references |
|||
Impediments:
1.
There
are many areas in
2.
Lack
of adequate information to farmers and consumers about the advantages of
organic agriculture, products, domestic and international market
information on suppliers, prices and quality and lack of easy market
access, discourages farmers from undertaking organic cultivation and
consumers from purchasing these products. Moreover, the production of
organic food requires considerable attention, care and skills and above
all, a good link with its market and small farmers cannot afford these
expenses.
3.
Consumer
unawareness, in addition to improper marketing, restrains the organic
products from obtaining higher rates, deterring the farmers from going in
for further cultivation. For instance, organic products are sold to the
middleman and are being marketed along with other chemically-grown
products. Sometimes the chemically-grown products which look healthy and
attractive, in spite of having alarmingly high level of pesticide residue,
fetches higher prices than the poorly looking-organic products due to lack
of awareness among the consumers, who fail to differentiate between the
two.
-
Various certifying agencies like JAS, Ecocert and IMO, self-certifying NGO like Organic Farmers Association of India (OFAI), government agencies APEDA, and different small co-operative agencies formed by the farmers - operate independently, making the process tedious. In addition, this procedure is quite expensive. Thus, small farmers, who grow maximum part of their produce organically, cannot afford to obtain these certificates.
5.
Organic
food is more expensive compared to regular products, since huge cost is
involved to transform chemically-processed land and free it of residual
pesticides. Besides, post harvest techniques need to be contamination
free, that is, food handlers, processors, and retailers must stick to the
standards that maintain the integrity of organic agriculture products,
resulting in hiking the market price of the final organic products.
6.
The
infrastructure and competencies to support organic conversion are still
generally lacking as insufficient attention has been provided towards
standards and certification development, production activities and proper
handling of market supply chains. Inadequate training facilities, organic
farmers’ field schools and lack of multidisciplinary research work
dissuade farmers from implementing the organic farming system and its
further extension.
7. Organic agriculture has not been given adequate attention in agricultural policy. Firstly, there is no government assistance for the promotion of organic agriculture, as it exists for conventional agriculture in the form of subsidies, agricultural extension services and official research. Secondly, during the transition period of 2-3 years, farmers are not able to use any inorganic fertilizers or agrochemicals, rendering the crop yield to decline. As a result, farmers have to suffer losses. Thus, in the absence of any kind of compensation to support the farmers during the transition period, organic farming obviously becomes absolutely unattractive.
Conclusion:
The
organic production system is designed to enhance biological activity
within the whole production system and maintain long-term soil fertility,
duly relying on renewable resources in the locally organised agricultural
systems. The benefits of organic farming are relevant both to developed
nations (environmental protection, biodiversity enhancement, reduced
energy use and CO2 emission) and to developing countries like
(*: This note has been prepared by Miss Pallavi Oak with the inputs from Abhilasha Maheshwari)
References:
1.
Bhattacharyya P. and G. Chakraborty
(2005), ‘Current Status of Organic Farming in
2. Prasad Rajendra (2005), ‘Organic farming vis-à-vis modern agriculture’, Current Science, Vol. 89.
3. P. Ramesh, Mohan Singh and A. Subba Rao (2005),‘Organic farming: Its relevance to the Indian context’, Current Science, Vol. 88.
4.
Rai (Dr.) Mangala (2005), Millennium
Guest Lecture on ‘Organic Farming: Potentials And Strategies delivered
at
5. The International Federation of Organic Agriculture Movements (IFOAM), the Swiss Research Institute of Organic Agriculture FiBL, and the Foundation Ecology & Farming (SÖL), Germany (2004, 2005, 2006), ‘The World of Organic Agriculture Statistics and Emerging Trends’.
|
Annexure
1: Organic Cultivation: A Brief Coverage |
|||||||||
|
Countries |
Area
under organic management |
Organically
cultivated area as a percentage of total agriculture area |
Number
of Organic farms |
||||||
|
|
2005-06 |
2004-05 |
2003-04 |
2005-06 |
2004-05 |
2003-04 |
2005-06 |
2004-05 |
2003-04 |
|
|
12.13 |
11.30 |
10.00 |
2.71 |
2.48 |
2.20 |
1832 |
1380 |
1380 |
|
|
0.05 |
0.04 |
0.05 |
0.26 |
0.24 |
0.33 |
820 |
NA |
800 |
|
|
2.80 |
2.80 |
2.96 |
1.58 |
1.70 |
1.70 |
1824 |
1781 |
1179 |
|
|
0.89 |
0.93 |
0.95 |
0.22 |
0.22 |
0.23 |
8035 |
11998 |
6949 |
|
|
0.69 |
0.70 |
0.72 |
4.39 |
4.42 |
4.22 |
4010 |
4017 |
4057 |
|
|
0.77 |
0.73 |
0.70 |
4.52 |
4.30 |
4.10 |
16603 |
16476 |
15628 |
|
|
0.95 |
1.05 |
1.17 |
6.22 |
6.86 |
8.00 |
36639 |
44043 |
49489 |
|
|
0.53 |
0.55 |
0.51 |
1.80 |
1.86 |
1.70 |
11059 |
11377 |
11177 |
|
|
3.47 |
0.30 |
0.30 |
0.60 |
0.06 |
0.06 |
1560 |
1050 |
2910 |
|
|
0.11* |
0.08 |
0.04 |
0.06* |
0.05 |
0.03 |
5147* |
5147 |
5147 |
|
|
0.05 |
0.05 |
0.00 |
0.05 |
0.05 |
0.05 |
250 |
250 |
250 |
|
|
0.02 |
0.02 |
0.02 |
0.72 |
0.19 |
0.19 |
NA |
500 |
460 |
|
|
0.29 |
0.03 |
0.00 |
0.56 |
0.66 |
0.10 |
4539 |
4539 |
NA |
|
All
world |
31.50 |
26.46 |
24.07 |
NA |
NA |
NA |
622782 |
558449 |
462475 |
|
*:
Provisional, NA: Not available |
|||||||||
[1]
Lampkin, Nicholas, C. Foster, S. Padel and P.Midmore (1999). The
Policy and Regulatory Environment for Organic Farming in
[2]
A study conducted by The International Federation of Organic
Agriculture Movements (IFOAM), the Swiss Research Institute of Organic
Agriculture FiBL, and the Foundation Ecology & Farming (SÖL),
[3]
'National Study:
Highlights of Current Economic Scene
AGRICULTURE
The
central government has managed to purchase just 6,40,000 tonne of wheat
during March 20 - April 9,
2006 as against 1.3 million tonnes a year ago on account of current open
market prices exceeding the government’s minimum support price (MSP) of
Rs 650 per quintal by almost Rs 100 - Rs 150 per quintal. Wheat
procurement started in Madhya Pradesh and Rajasthan on March 20, 2006 and
in
The
Ministry of Agriculture has discarded
The
records available with the national egg co-ordination committee (NECC)
have revealed that the poultry industry in
The prices of live chicken that hit rock bottom last month amidst bird flu scare have begun to move upwards with thee broiler prices touching to Rs 30 a kg. As per the State Broiler Co-ordination Committee (BCC) in Tamil Nadu, the production cuts resorted to by the poultry producers immediately during February and March 2006 have triggered the current price recovery for the live birds. The ending of religious austerities in the Hindu calendar as well as Easter celebration have also contributed to this price hike to some extent.
A
bumper onion harvest has caused a steep fall in onion prices in
The Centre has planned to set up a single investment window to approve economic zones for agriculture, food processing, horticulture, medicinal plants and rural business hubs to boost exports and generate employment opportunities in the country. The move aimed at simplifying the process for setting up these zones, which is currently controlled by five different ministries namely, ministries of commerce, agriculture, food processing, panchayati raj and health. The plan costing Rs 60-70 crore would seek funding either from National Horticulture Mission or from the ASIDE fund (Assistance to States for Infrastructure Development).
A
comprehensive long-term rehabilitation package would be announced by the
central government in two months, targeting 30 districts in four states,
where a large number of suicides by farmers have been reported in the
recent past. The package would cover 15 districts in Andhra Pradesh, 6
each in
In the backdrop of recent outbreak of H5N1 strain of avian flu, the National Commission on Farmers (NCF) has demanded to set up of a National Agricultural Biosecurity Fund, which would be used for establishing an Offshore Genetic Screening Centre (OGSC) for animals. The fund worth Rs 1,000 crore would also be utilised for strengthening infrastructure for sanitary and phyto-sanitary measures and upgrading facilities for plant, animal and fish quarantine. The Commission has also sought establishing National Agricultural Biosecurity System comprising National Agricultural Biosecurity Council (NABC), National Centre on Agricultural Biosecurity (NCAB) and National Agricultural Biosecurity Network (NABN), which would deal with analysis, aversion and management of risks apart from setting up an early warning system.
The
state government of
INFRASTRUCTURE
Petroleum
and Petroleum Products
Reliance
and Schlumberger have approached the finance ministry to exempt surveys
and exploration of oil and gas from the purview of service tax on the
ground that oil companies like Oil and Natural Gas Corporation Ltd (ONGC)
and Indian Oil Corporation (IOC) do not allow them to factor in the tax
for undertaking such surveys. In case the survey is within
Coal
The
government has plans to going to allot 28
An
Expert Committee on coal sector reforms, in Part A of its report submitted
to the coal ministry, has favoured an independent regulatory mechanism for
coal pricing, especially for the power sector that consumes about 80 per
cent of total coal produced in the country. Coal prices at present are
fixed by the coal ministry in consultation with coal PSUs Coal India
Limited (CIL) and Singareni Collieries Company Ltd (SCCL), determined on
the basis of costs incurred in coal production from different mines in a
coal company plus a reasonable amount of profit. For the sake of evolving
a pricing mechanism, the committee has divided the consumers into two
categories - Class A and Class B - with the former being the power sector
consumers and latter being other coal consumers. Interestingly, while the
committee has favoured 60 per cent linkage for Class B consumers, the
Planning Commission in its earlier report has favoured 80 per cent linkage
for them.
Ports
The
Tuticorin port has become the third largest in the country, after JNPT and
Chennai ports, in terms of size. About the port performance, it has
handled 3.21 crore TEUs (twenty foot equivalent units) of container
traffic during 2004-05, 4.47 per cent higher than the previous year and
cargo handled has risen by 8.4 per cent from 1.58 crore tonnes to 1.71
crore tonnes. The net surplus after tax has been a record high of Rs 73.34
crore and the operating ratio, an indicator of the efficiency, has been 39
per cent. The port net worth has reached an all-time high of Rs 522.15
crore against Rs 452.19 crore. The port is expected to grow at 20 per cent
in 2005-06.
Tuticorin
port has plans for a major expansion with an investment of over Rs 4,000
crore. The expansion plan will be carried out in two phases. The work in
the first phase includes setting up a new terminal and dredging at a cost
of Rs 835 crore, is expected to be taken up soon. The Rs 450-crore
deepening of the draft to 12.8 metres, a part of the first phase of the
expansion scheme under the National Maritime Development Project, has
received clearance from the environment ministry. The port expects the
work to be completed by December 2007 and had sought a budgetary support
of Rs 225 crore for the same. The second phase of the Rs 3,300-crore
expansion from 2007-2012 would involve deepening the draft to 14.5 metres
for which a pre-feasibility study would be undertaken. The work order for
the study had been issued and is expected to be completed in three months.
– FE
The Paradip port has handled 33.11 million tonnes of traffic during 2005-06, surpassing 30.10 million tonnes handled a year ago, representing a growth of 10 per cent – the traffic handled included 21.6 million tonnes of export and 11.4 million tonnes of import.
Roads
The
ambitious National Highways Development Programme (NHDP) of the government
has been running behind schedule and the second phase of the project has
been also suffering from cost over-run. In the first phase of NHDP,
against a target of 893 km to be completed by February 2006, only 672 km
could be built. The Golden Quadrilateral (GQ) project linking
INFLATION
The annual point-to-point inflation rate based on wholesale price index (WPI) has gone down to 3.51 per cent for the week ended April 1, 2006 from 3.96 per cent during the previous week. The inflation rate was at 5.70 per cent in the corresponding week last year.
The WPI in the week under review has increased considerably by 0.4 per cent to 197.7 from 197 in the previous week (Base: 1993-94=100). The index of primary articles’ group (weight 22.02 per cent) has risen substantially by 1.3 per cent to 195.7 from the previous week’s level of 193.1, mainly due to an increase by 1.9 per cent in the price index of food articles. The index of ‘food articles’ has increased to 199 from 195.3 in the previous week, mainly due to an increase in the prices of urad, condiments and spices, moong, fruits and vegetables, arhar, gram and bajra. Similarly, the index of non-food articles has risen marginally by 0.1 per cent to 174.8 from 174.7 in the earlier week, due to an increase in the prices of mesta, raw jute and raw cotton. The index of ‘fuel, power, light and lubricants’ group (weight 14.23 per cent) has also increased by 0.1 per cent to 316.7 from 316.3 in the previous week. The index of ‘manufactured products’ group constituting the maximum of 63.7 per cent of total weight, has too gone up a tad by 0.1 per cent to 171.8 from the previous week’s level of 171.7. The major groups, which contributed to this increase, were the textiles, ‘non-metallic mineral products’ and ‘machinery and machinery tools’.
The latest final index of WPI for the week ended February 4, 2006 has been revised downwards; as a result both, the absolute index and the implied inflation rate stood at 196 and 3.98 per cent as against their provisional levels of 196.2 and 4.08 per cent, respectively.
The average rate of inflation in the year 2005-06 has stood at 4.5 per cent. Similarly, the point-to-point rate of inflation has stood at 4 per cent, a percentage point lower than the estimated rate of 5 per cent in the Economic Survey 2005-06.
BANKING
The
week-long strike called by over 2
Nabard’s
refinance for commercial banks has increased to Rs 4,289 crore in 2005-06
from previous year’s Rs 2,469 crore. The bank hopes that the demand for
refinance from commercial banks would increase further.
PUBLIC
FINANCE
The
central government has released over 87 crore rupees to twenty-six small
and medium towns across three states to take up various schemes under the
urban infrastructure development scheme for small and medium towns (UIDSSMT).
The amount which is the first installment of the central government’s
share under the UIDSSMT has been released to Andhra Pradesh,
As
proposed by the Finance Minister in the budget proposals 2006-07, the
government has constituted an expert committee to look into the potential
of the gem and jewellery industry and the prevalent taxation practices in
this sector in the country and abroad and to make suitable recommendations
to enable ![]()
FINANCIAL
MARKET
Capital
Markets
Primary
Market
The
Reliance Petroleum’s IPO has been subscribed 7.5 times at the end of
first day of its opening. However, the participation of the retail
investors has not been impressive at 17 per cent of their entitlement,
while the qualified institutional buyers (QIB) portion has been subscribed
11 times and the high net worth portion has been subscribed 8.32 times.
Plethico
Pharmaceuticals Limited has tapped the market, on April 13, with its
public offer of about 75.94 lakh equity shares in a price band of Rs 280
to Rs 300 per equity share; the issue closes on April 17.
Lokesh
Machines Limited, on April 10,has tapped the market with its public issue
of 30 lakhs equity shares in a price band of Rs 130 to Rs 140 per equity
share. The issue closes on April 13,2006.
Secondary
Market
High
international crude oil prices, aggressive FII selling, and the weak trend
in other Asian stock exchanges have resulted into a highly volatile stock
market over the week. On April 12, the BSE sensex has lost a whooping
306.82 points to settle at 11,355.73 points and the nifty has also
registered a fall by 98.45 points to settle at 3380 points, triggered by
massive FII selling to the extent of Rs 421.70 crore. Meanwhile, over the
week, the sensex has declined by 3.04 per cent to settle at 11237.73
points, while the nifty has recorded a decline of 3.16 per cent to settle
at 3345.5 points.
Among
the sectoral indices of the BSE with exception of BSE Metal and BSE Oil
and Gas, which have witnessed a rise of around 2.51 per cent and 0.29 per
cent, respectively, all others have closed the week in negative territory,
with BANKEX registering the highest fall of 4.75 per cent (8290.46
points), followed by BSE IT at 4.67 per cent (3896.32 points). Meanwhile,
as compared with sensex, the BSE Small-Cap and BSE Mid-Cap have registered
a decline of 1.97 per cent and 2.97 per cent, respectively.
The
Sebi has revised the minimum shareholding norms, wherein companies having
market capitalisation of Rs 1,000 crore and those having 20 million shares
listed have been exempted from the minimum 25 per cent public shareholding
requirement. Further, companies which have issued shares in initial public
offers under Rule 19 (2) (b) of the Securities Contract (Regulations)
Rules, 1957 and those who are tending to get listed under the rule have
also been excluded from the shareholding requirement.
The
tight market liquidity condition and the allure of fixed maturity plans
offered by mutual funds have taken away the sheen of liquid funds, which
have witnessed net outflows worth Rs 11652 crore in March. However, the
total mutual fund asset under management has recorded a growth of 6.5 per
cent to Rs 231862 crore during the month.
During
the week, the FIIs have been huge sellers in the equity market to the
extent of Rs 1583.6 crore with purchases worth Rs 8059.2 crore and sales
of Rs 9642.7 crore. On the other hand, mutual funds have been net buyers
in the equity market to the tune of Rs 391.75 crore with purchases worth
Rs 2098.04 crore and sales aggregating to Rs 1706.29 crore.
Derivatives
During
the week under review, the total turnover at the NSE’s F&O segment
has declined to Rs 128,245 crore from Rs 148,850 crore, though the daily
average turnover has increased in the holiday-shortened week to Rs 42748
crore from Rs 37212 crore in the previous week. As compared with the
previous week, the turnover of the index futures have increased to Rs
40,654 crore from Rs 32,910 crore, while the turnover in stock futures
have declined to Rs 74,018 crore from Rs 103,349 crore.
Government
Securities Market
Primary
Market
The
RBI has conducted sale of a new 10-year government paper and has also
re-issued 7.50 per cent 2034 for a notified amount of Rs 5,000 crore and
Rs 3,000 crore, respectively. The cut-off yield for the new 10-year
government paper and 7.50 per cent 2034 paper has been set at 7.59 per
cent and 7.97 per cent, respectively.
During
the week, the RBI has, under the regular auction, mobilised Rs 2107.62
crore through 91-day treasury bill at a cut-yield of 5.4889 per cent and
Rs 1000 crore from 364-day treasury bill with a cut-off yield of 6.0611
per cent.
Secondary
Market
Apprehensions
over the impending decision over the interest rate in the RBI’s monetary
policy, rising global crude oil prices and the rising US yields has kept
the market cautious over the week. In the initial part of the week, the
market participants have been cautious due to the auction of central
government dated security worth Rs 8,000 crore. However, increased
government spending towards the salary payments and the RBI intervention
in the forex market resulted into robust cash surplus with the market.
Consequently, the call rates have moved around the reverse repo rate for
most part of the week to close at 5.50-5.60 per cent. Meanwhile, the
auction outflows worth Rs 8,000 crore also have not been able to affect
the market liquidity. The amount placed under the repo has averaged to Rs
300 crore as against Rs 562 crore, while the daily average reverse repo
subscription has risen to Rs 52,300 crore from Rs 21,223 crore in the
previous week. Over the week, the weighted average YTM of 8.07 per cent
2017 paper has risen to 7.5609 per cent as on April 13 from 7.5397 per
cent as on April 7.
Bond
Market
Oriental
Bank of Commerce has raised Rs 500 crore, including the greenshoe option
of Rs 250 crore, capital through private placement of bonds.
Foreign
Exchange Market
The
huge FII outflows during the week coupled with high international crude
oil prices due to geopolitical risks surrounding
Commodities
Futures Derivatives
During
the week, in the commodity futures markets, high volatility has been
witnessed in the trading of pepper futures after rising in the initial
part of the week on account of short-covering, which was triggered by news
of active export buying in the spot market, the pepper futures have
declined in the later part of the week. On the other hand, the cardamom
futures have continued to fall mainly on account of weak fundamentals.
Meanwhile, despite the continuous weakness in the Asian rubber futures
market, the spot market movement of rubber has lifted the rubber futures
trading. The spot rubber prices are expected to touch the high level of Rs
90 due to strong domestic and export demand. High prices and the
accompanying bullish outlook is making growers hold on the stocks, thereby
leading to the supply crunch. Also, the global markets have scaled new
levels, which also influences the domestic market. Meanwhile, the
uncertainty over the FMC’s dictum against launching new contracts in
urad and tur as well as lesser additional margins for taking short
positions in comparison to long positions has resulted in to more selling
pressure on the urad and tur contract over the week.
INSURANCE
In a record breaking performance, the Life Insurance Corporation of India (LIC) in 2005-06 has generated three crore new policies against 2.39 crore policies in 2004-05. LIC has mobilised the first premium income (FPI) of Rs 18,085.48 crore as against Rs 12,000 crore in 2004-05. The company’s golden jubilee launch, Bima Gold, registered an unprecedented success story, crossing one crore policies in seven months since launch.
CREDIT
RATING
Crisil has assigned a real estate developer rating of ‘DA3’ to Mani Square Private Limited (MSPL). The assigned rating indicates that the developer has a good track record in executing real estate projects as per specified quality levels and transferring a clear title within the stipulated time schedule.
Crisil has reaffirmed the ‘FAA’ and ‘P1+’ ratings assigned to Kirloskar Brother’s fixed deposit programme and Rs 200 million commercial paper programmes. The reaffirmation by the agency follows the approval by the company’s board of directors on April 4,2006 to de-merge its Anti-corrosive Products Group into a separate entity.
Crisil has reaffirmed the ‘P1+’ rating assigned to Balrampur Chini Mills Limited’s Rs 200 million short-term debt programmes. The rating reaffirmation continues to reflect the company’s high operating capabilities, the benefits it derives from its favourable locations and a strong financial risk profile.
Crisil has assigned ‘AAA/Stable’ rating to CitiCorp Maruti Finance’s Rs 500 million non-convertible debentures issue. The assigned rating is based on the company’s ultimate majority ownership by Citigroup Inc. and its strategic importance to the ultimate parent company.
Care
has retained the credit rating of various bond issues of Maharashtra
Patbandhare Vittiya Company Ltd. (MPVC), Maharashtra Water Conservation
Corporation (MWCC) and Maharashtra Jeevan Pradhikaran (MJP) at ‘BB
(SO)’. The above mentioned ratings are based on unconditional and
irrevocable guarantee of government of
Care
has re-affirmed the rating of outstanding bond issue of EDC Ltd. at ‘A
(SO)’; this rating is based on credit enhancement in the form of
unconditional and irrevocable guarantee of government of
Care has reaffirmed the ‘AAA’ rating assigned to the various outstanding debt instruments of Small Industries Development Bank of India (SIDBI). The agency has also retained ‘AAA (FD)’ rating for the fixed deposit programme as well as the ‘PR1+’ rating assigned to the commercial paper program of SIDBI. The rating continues to reflect SIDBI’s position as the apex financial institution for the small-scale industries (SSI), the demonstrated support received from government, its high capital adequacy and comfortable liquidity.
Care has assigned ‘AA+’ rating to the proposed Rs.250 crore (Series II) Tier II subordinated bond issue of Vijaya Bank. The agency has also retained the ‘AA+’rating assigned to the outstanding Rs.250 crore (Series I) Tier II bond issue of the bank. The rating factors in the government’s ownership of the bank, long standing track record, comfortable capital adequacy, superior asset quality and strong solvency position.
Fitch
Ratings has assigned an ‘AAA (
Fitch
Ratings has affirmed the PTC India Limited's short-term debt rating on its
Rs 200 million programme at 'F1+(
CORPORATE
SECTOR
Indian Oil Corporation (IOC) and Haryana State Industrial Development Corporation have signed a Memoramdum of Understanding for developing a petrochemicals hub with an investment of Rs 25,000 crore in Panipat.
Trend Micro, an anti-virus and internet content security software and services firm, has entered into a global agreement with Ericsson to offer Trend Micro mobile security solution. Ericsson will incorporate Trend Micro mobile security solution into Ericsson mobile device as part of its mobile data solution portfolio, offered to enterprises and mobile operators.
Zensar
Technologies has tied up with the world’s third largest information
technology services provider solutions Fujitsu Services to cater
Fujitsu’s customers in Europe, West Asia and
Chevron Corporation, the world’s fifth largest integrated energy company, has signed an agreement with Reliance Industries to pick up 5 per cent shares in Reliance Petrochemicals Limited for nearly Rs 1,320 crore ($ 300 million).
Royal
Orchid Hotels has acquired 51 per cent shares in Maruti Comforts and Inn,
Pune based Thermax, a global solutions provider in energy and environment engineering, is setting up its second major plant in Vadodara in Gujarat Industrial Development Corporation premises.
According to PRIME database, a leading data base in the primary capital market, the Indian corporate sector have mobilised around Rs 23,684 crore through a mix of equity offerings in the financial year 2005-06, a growth of 10.56 per cent than the previous years Rs 21,422 crore.
Grasim Industries, the flagship company of Aditya Birla Group, will invest about Rs 560 crore to double the capacity of Aditya Cement from the current 1.5 million tonne per annum.
ABG Shipyard has secured an order of Rs 270 crore for construction of six anchor handling tug vessels each at a price of $ 9.99 million from Sea Tankers Management Co, a part of ship owning company John Fredriksen’s Group.
Power equipment major Bharat Heavy Electricals Limited has secured an order worth Rs 1,200 crore from GIPCL for setting up two units of 125-mega watt (mw) each. GIPCL has placed an order for setting up two units of 125 mw each (Units iii and iv) for its Surat Lignite Thermal Power Station expansion project.
Associated Cement Companies’s (ACC) total income has risen by 19.6 per cent to Rs 1,381 crore for the first quarter ended March 2006. ACC has changed its accounting year from April-March to January-December. ACC has reported a 42 per cent increase in net profit at Rs 235 crore during January-March 2006. ACC will invest Rs 400 crore to expand capacity by one million tonne a year at its factory in Lakheri, Rajasthan and set up a 25-mega watt coal based captive power plant.
MphasiS BFL has reported a 22 per cent rise in sales revenue at Rs 250.50 crore for the fourth quarter ended March 2006 and net profit has increased by 14 per cent at Rs 35.16 crore over the same period previous year. The MphasiS BFL Group’s consolidated revenues for 2005-06 have increased by 23 per cent to Rs 94.011 crore and net profit has stood at Rs 149.86 crore, a growth of 20 per cent over the same period previous year.
iGate Global Solutions has reported a whooping 111 per cent rise in net profit for the fourth quarter ended March 2006 to Rs 4.7 crore.
Sasken
Communication Technologies Limited has posted a decline of 42 per cent in
its net profit to Rs 6.29 crore for the fourth quarter of the financial
year 2005-06.![]()
EXTERNAL
SECTOR
According
to the World Trade Organisation's ‘World Trade Report 2005, a robust
growth in merchandise exports in 2005 has resulted in India’s share in
world exports to inch up to 0.9 per cent from 0.8 per cent in 2004. In
services,
The top six positions in world merchandise exports has been maintained by Germany ($976 billion), the US ($904.3 billion), China ($762 billion), Japan ($595.8 billion), France ($459.2 billion) and Netherlands ($401.3 billion).
The report has warned that the prospects of trade did not seem too bright in 2006, as a further rise in energy costs during the year cannot be excluded. It noted that crude oil prices reached a new peak in the first quarter of 2006, already exceeding the annual average of 2005 by 10 per cent.
According
to World Trade Organisation (WTO) forecast, global trade may grow at 7 per
cent in 2006, up from last year’s revised 6 per cent expansion. In its
annual review of trade trends, the WTO said that the outlook had been
based on expected world economic growth of 3.5 per cent, slightly faster
than the 3.3per cent rise in 2005. It said in the report that world trade
was expected to benefit from this slightly stronger economic growth — in
particular in the European Union.
However,
it has cited a number of downside risks, including the possibility of
The
debate over special economic zones is set to intensify further with the
finance ministry once again questioning several provision of the SEZ Act,
2005, including the provision to allow re-construction or transfer of an
existing unit from the local area into the SEZ.
LABOUR
According
to the statistics of the Asian Productivity Organisation,
|
Labour
Productivity in Asian Countries in 2004 |
||
|
Country |
GDP/Person
(in
US $) |
Per
cent change in real GDP per person employed |
|
|
3.10 |
5.85 |
|
|
3.95 |
8.02 |
|
|
3.65 |
5.87 |
|
|
5.14 |
3.01 |
|
Source:
Asian Productivity Organsiation |
||
According
to the statistics, the productivity indices of
The ongoing issue of the reservation of jobs for SC, ST and OBCs in the private sector has been opposed by some of the corporate giants like Tata Sons Ltd and Bajaj Auto Ltd, stating that such a reservation would divide the country into segments. Instead, they have favoured bringing about a systematic change in the education set-up, strengthening small and medium enterprises and advocated a system that provides equal opportunities to all the underprivileged, not necessary based on caste.
INFORMATION
TECHNOLOGY
The
domestic IT market will grow by 23 per cent to $4.3 billion in the current
fiscal, according to the IT User 2005 Survey released by Nasscom. Few
organisations in
India’s second largest IT company Infosys Technologies has announced a 30 per cent growth in its net profit in 2005-06 to Rs 2,458 crore against Rs 1,892 crore in the previous fiscal. The company has declared a 1:1 bonus. Celebrating 25 years since its incorporation, the company declared a special silver jubilee dividend of 600 per cent (Rs 30 on every Rs 5 share). This will imply an outflow of Rs 827 crore. It also announced a final dividend of 170 per cent (Rs 8.50 per share), which will take the total dividend in the fiscal to 900 per cent (Rs 45 per share) amounting to an outgo of Rs 1,238 crore.
TELECOM
The Aditya Birla Group has agreed to buy Tata group’s entire 48.14 per cent stake in Idea Cellular for Rs 4,406 crore (at Rs 40.50 per share), marking an end to the spat between two of India’s largest corporate houses.
|
Macroeconomic Indicators |
|
Table
1 : Index Numbers of Industrial Production (1993-94 =100) |
|
Table
2 : Production in Infrastructure Industries (Physical Output Series) |
| Table 3: Procurment, Offtake and Stock of foodgrains |
|
Table
4: Index Numbers of Wholesale Prices (1993-94 = 100) |
|
Table
5 : Cost of Living Indices |
|
Table
6 : Budgetary Position of Government of India |
|
Table
7 : Government Borrowing Programmes and Performance |
|
Table
8 : Scheduled Commercial Banks -
Business |
|
Table
9 : Money Stock : components and Sources |
|
Table 10 : Reserve Money : Components and Sources |
|
Table
11 : Average Daily Turnover in Call Money Market |
|
Table
12 : Assistance Sanctioned and Disbursed by All-India Financial
Institutions |
|
Table
13 : Capital Market |
|
Table
14 : Foreign Trade |
|
Table 15 : India's Overall Balance of Payments |
|
Table
16 : Foreign Investment Inflows |
| Table 17 : Foreign Collaboration Approvals (Route-Wise) |
| Table 18 : Year-Wise (Route-Wise) Actual Inflows of Foreign Direct Investment (FDI/NRI) |
|
Table
19 : NRI Deposits - Outstandings |
|
Table
20 : Foreign Exchange Reserves |
|
Table 21 : Indices REER and NEER of the Indian Rupee |
|
Table
22 : Turnover in Foreign Exchange Market |
| Table 23 : India's Template on International Reserves and Foreign Currency Liquidity [As reported under the IMFs special data dissemination standards (SDDS) |
| Table 24 : Settlement Volume and Netting Factor for Government Securities Transactions Settled at CCIL - Monthly, Quarterly and Annual Basis. |
| Table 25 : Inter-Catasegory Distribution of All Types of Trade in Government Securities Settled at CCIL (With Market Share in Respective Trade Types) |
| Table 26 : Category-wise Market Share in Settlement Volume of Government Securities Transactions (in Per Cent) |
| Table 27 : Settlement Volume and Netting Factor for Total Forex Transactions Settled at CCIL - Monthly, Quarterly and Annual Basis. |
| Table 28 : Inter-Category Distribution of Total Foreign Exchange Transactions Settled at CCIL (With Market Share in Respective Trade Types) |
|
Memorandum Items |
*These statistics and the accompanying review are a product arising from the work undertaken under the joint ICICI research centre.org-EPWRF Data Base Project.
We will be grateful if you could kindly send us your feed back at epwrf@vsnl.com